Clock
Embark on a spectacular journey around the globe with “Clock,” your go-to source for unearthing spectacular travel destinations. Penned with the fervor of an adventure traveller, the posts in this series help you explore hidden gems, allowing you to plan the vacation of a lifetime. So, while the clock ticks, let your sense of adventure surge with every twist and turn of these travel-oriented tales, inspiring wanderlust and feeding your inherent need to explore the unknown.

History of Clocks
Let’s take a trip down memory lane and explore the history of an everyday device that you likely don’t give a second thought to – clocks.
Origin and Development of Clocks
So, where did it all begin? The origins of clocks trace back to ancient civilizations, where they used simple sundials and water clocks to track time. And if you think about it, these early models were ingenious for their time. Yes, they relied on the sun or water’s flow for measurements, but these primitive devices laid the foundation for what was to come. The journey evolved from sundials and water clocks to sand-filled hourglasses, candle clocks, and mechanical clocks.
Advancements in Timekeeping
Venture ahead into the 14th century, and you landed on the concept of mechanical clocks. These timekeeping devices had their power coming from weights. Then the pendulum clock was introduced by Dutch scientist Christiaan Huygens in 1656, becoming the most accurate timepiece until the 1930s. You wouldn’t believe the magic that happened during the Industrial Revolution in the late 18th century; the advent of electricity changed clocks’ working mechanism forever.
Influence on Civilization
Now, why does this matter? Because, without these advancements, our everyday routines would have been so different. Clocks significantly impacted trade, transportation, and even the structure of society. Remember, this was before cellphones, computers, or digital watches. Cities synchronized time, which meant trains could run seamlessly, businesses operated on time, and people scheduled their day around the clock.
Different Types of Clocks
Let’s delve into this topic deeper and look at the different types of clocks that have existed.
Mechanical Clocks
Mechanical clocks are fascinating, aren’t they? They remind us of an era where craftsmanship prevailed over mass production. These clocks used gears and wheels driven either by weight or spring, linked to an escapement. The pendulum or balance wheel regulated the speed of the clock.
Quartz Clocks
Fast forward to the 20th century, the quartz clock was born. Driven by the piezoelectric properties of quartz crystal, these clocks presented a phenomenal leap in timekeeping accuracy over their mechanical predecessors.
Atomic Clocks
Now let’s talk science. You see, Atomic clocks utilize the vibrations of atoms to measure time ridiculously precisely, making them the most accurate timekeeping devices known to man. These don’t tick in nanoseconds or milliseconds but in billionths of a second!
Digital Clocks
Digital clocks, on the other hand, ditch the traditional clock face altogether. They display time as numbers, usually on an LED or LCD screen. It is a common sight, they’re everywhere – your phone, computer, oven, car dashboard, just everywhere you look.
Components of a Clock
Now, let us dissect a clock and look at its components.
Face and Hands
The face is the most visible part of a clock and what we’re most familiar with. Depending on the type, you have the numbers laid out and two or three hands that move around, indicating hours, minutes, and sometimes seconds.
Movement Mechanism
Don’t get fooled by the calm exterior; there’s a lot going on inside a clock. The movement mechanism, driven either by weight, spring, or electricity, is the heart of a clock that brings it to life.
Power Source
Be it the coiled spring of a mechanical clock or the crystal of a quartz clock, or a plain old battery for your digital clock, the power source is what drives these timepieces.
How a Clock Works
Time to lift the veil and see how these complex devices work.
Operation of Analog Clocks
In an analog clock, the power source moves the gears, which in turn move the clock hands at different but constant speeds. The ticking you hear is all about the escapement and pendulum or balance wheel doing their jobs.
Working of Digital Clocks
For digital clocks, electricity makes the crystal inside vibrate at a constant frequency. The circuits inside then convert these vibrations into pulses which then get translated into what you see as time on the display.
Functioning of Atomic Clocks
Atomic clocks are a bit more complex. They measure the vibrations of atoms (cesium or rubidium, for example) and use this as their ‘tick.’ Each ‘tick’ is incredibly consistent, leading to an extremely precise way of measuring time.

Significance of Clocks in Society
Into the society we live in, and you discover the crucial roles clocks play.
Timekeeping and Productivity
For one, the concept of timekeeping has enabled us to structure our days. It has increased productivity and efficiency, from workplaces to schools and households.
Clocks in Public Spaces
Clocks in public spaces like stations, offices, and buildings synchronize the community’s activities, ensuring that everything runs smoothly.
Impact on Cultural Events
Think about rituals, festivals, or events. They all have timings attached to them – from New Year’s countdown to remembering moments of historical importance, clocks are integral in marking milestones.
The Art and Science of Clockmaking
This brings us to the craft of clock making, an amalgamation of art and science.
Craftsmanship in Clockmaking
Just picture the intricacy of gears, screws, and springs put together by skilled craftsmen in mechanical clocks. Even today, watchmakers carry forward this tradition, passing it down generations.
Technological Changes in Clockmaking
With every technological advancement, clockmaking has adapted, merging tradition with innovation.
Famous Clockmakers and Their Constructions
Throughout history, some clockmakers left indelible marks. From the Huygens pendulum clock to Harrison’s sea clock, which eventually solved the longitude problem for seafarers, to the present-day atomic clock creators.
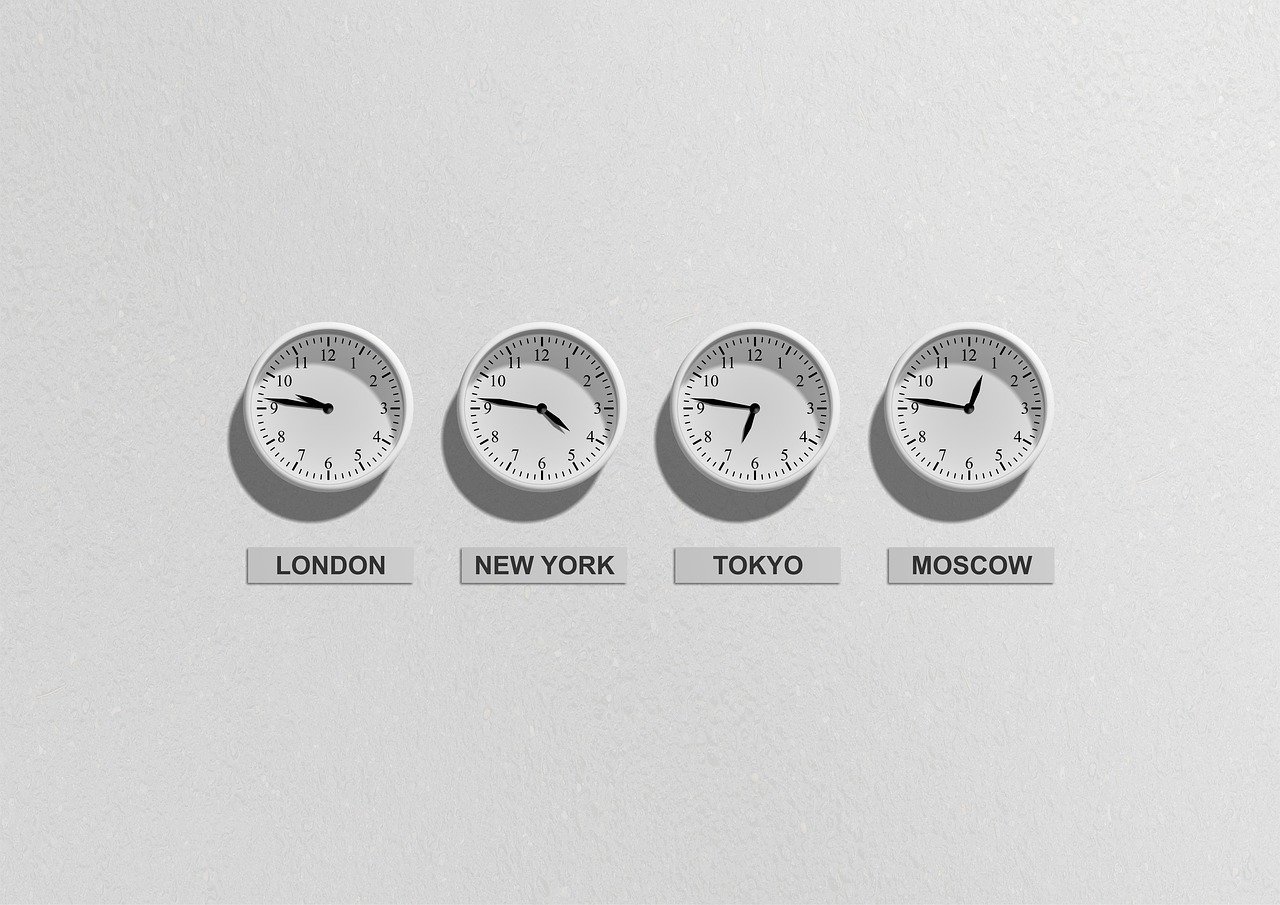
Famous Clocks Around the World
Famous clocks are not just timekeepers but architectural marvels and destination landmarks.
Big Ben in London
Big Ben, the clock at the north end of the Palace of Westminster in London, is one of the most famous clocks and a beloved symbol of the city.
The Grandfather Clock
The Grandfather Clock, also known as the longcase clock, is a classic of home decoration and a marvel of mechanics with its pendulum held inside the tall case.
The Swatch Art Peace Hotel Clock in Shanghai
Then there’s the Swatch Art Peace Hotel Clock in Shanghai, known for its unique fusion of modern design and traditional Chinese elements.
The Prague Astronomical Clock
The Astronomical clock in Prague is not just a clock but a brilliant example of medieval engineering, showcasing astronomical events.
The Flower Clock in Geneva
The Flower Clock situated in Geneva, Switzerland, is another wonder, a working clock made of various flower types.
Clocks in Literature and Arts
Delve into the realms of literature and arts, and you can see the influence of clocks.
Clocks as Symbolism in Literature
Many novels, poets use clocks as significant symbols. They often denote the passage of time, indicating inevitable change, mortality, or even the mechanical nature of society.
Clocks in Visual Arts
The hands, face, or the mechanical intricacies of a clock are often represented in paintings, drawings, or installations, reflecting different interpretations.
Time and Clocks in Movies
In the cinematic world, from ticking time bombs to countdown timers, clocks often heighten the drama, serving as visual metaphors and adding another layer to the narrative.
Clocks and Travel
Clocks play a fundamental role, especially in this era of global travel and exploration.
Time Zones and World Travel
Time zones, willfully represented by clocks, keep us aware of the local time in far-off lands, out of sync with our own immediate environment.
Role of Clocks in Navigational Systems
For the sea-faring explorers of old to today’s GPS technology, accurate timekeeping has always been at the center of navigation.
Impact on Travel Planning
From flight schedules to hotel check-ins, precise timekeeping ensures the seamless operation of the tourism industry, paving the way for excursions and adventures of all kinds.
Analog vs Digital Clocks for Travellers
Whether you prefer the aesthetic of an analog wristwatch or the practicality of a digital display, every traveler understands the importance of keeping track of time.
Future of Clocks
Looking ahead, the future of clocks promises fascinating opportunities.
Smart Clocks and IOT
Think smart clocks that interact with other devices in your home, from brewing your morning coffee to managing your schedule.
Atomic Clocks and the Precision of Time
The atomic clock technology builds foundation for many of today’s most advanced technologies, including GPS, telecommunications, and internet synchronisation.
Sustainability in Clockmaking
From energy-efficient designs to the use of sustainable materials, the clock industry is taking strides towards a greener future.
The Role of Clocks in Space Travel
With Mars missions and deeper space explorations, ultra-precise clocks will pave the way for interstellar communication and navigation systems.
That’s a wrap! And the next time you glance at a clock, remember, you are looking at a device that encapsulates centuries of human ingenuity and the relentless march of time.


