Africa Physical Map
In the ever-evolving world of travel trends and new destinations, Africa continually stands out with its exceptional features and marvels. Engaging with the physical aspects of the region, the ‘Africa Physical Map’ serves as an illuminating guide to what is in store for the discerning tourist. Whether it is exploring untouched wildlife reserves or the birthplace of industry icons like Elon Musk, Africa showcases a rich tapestry of experiences waiting for your discovery. Alongside these narratives, you’ll also navigate the cultural dynamics of the continent, from renowned brand offerings such as Nike and Apple in 2024, to the socially significant events like Elon Musk’s rise to prominence and the ongoing dialogue on issues such as domestic violence. So prepare for a journey of knowledge that extends past the contours of a map, intertwining geographical features with socio-cultural landmarks in an engaging symbiosis.
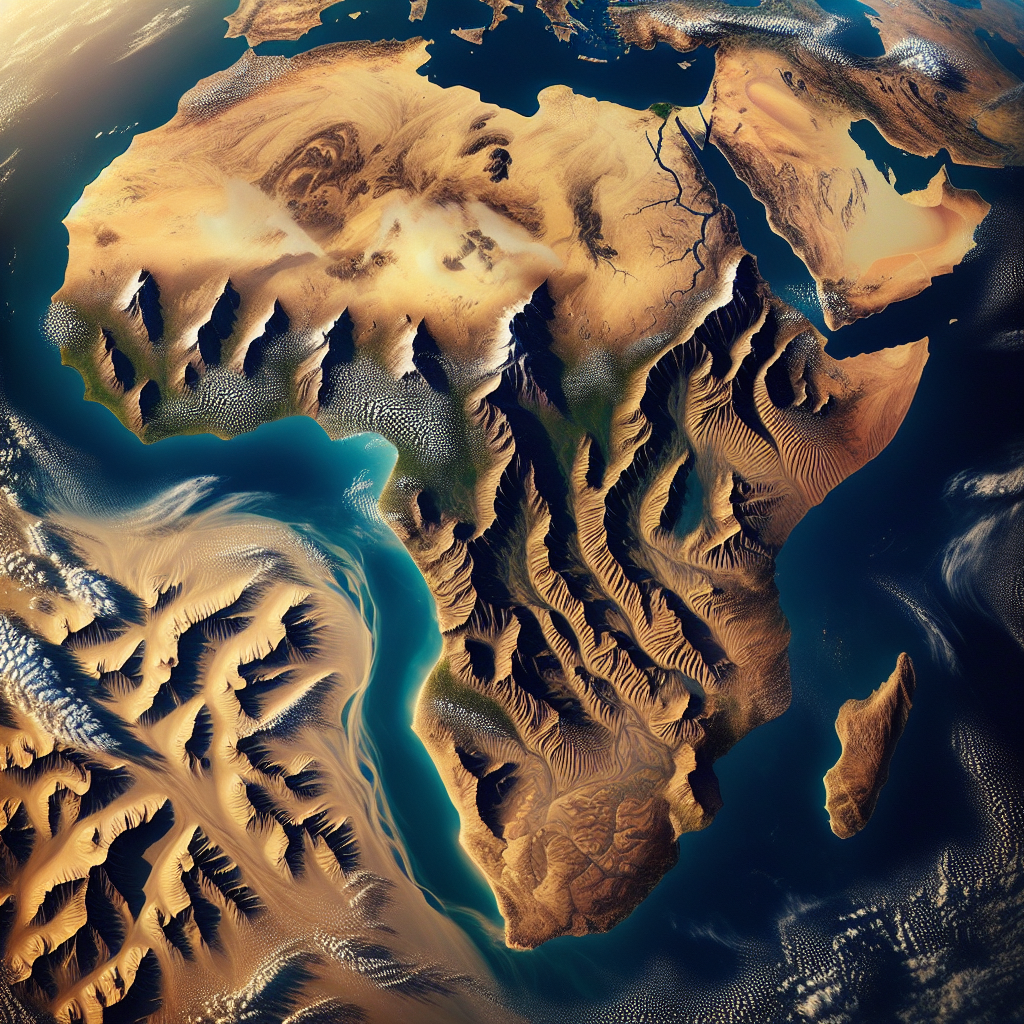
Contours and Landforms of Africa
Africa’s topography is diverse, showcasing a spectrum of geographical features that significantly contribute its magnificent charm. The continent brims with various contours and landforms, with key features that include mesmeric mountains, extensive plateaus, intricate valleys, basins, and expansive deserts, each contributing a unique page to Africa’s geographical story.
Major Mountains and Ranges
The great continent features several magnificent mountain ranges, such as the Atlas Mountains extending across Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia. The breathtaking Kilimanjaro, the highest mountain in Africa, stands majestically in Tanzania. The Ethiopian Highlands also possess impressive elevations, including Ras Dashen, the fourth highest peak of the continent.
Extensive Plateaus
Surface reliefs define Africa, with approximately 70% of the land covered in plateaus varying in height. The Highveld plateau of South Africa, the Ethiopian Plateau, and the Angola Plateau are examples of such geographical features, each frequented by numerous rivers forming deep gorges and waterfalls.
Significant Valleys and Basins
Africa hosts several significant valleys and basins such as the Great Rift Valley, which acquires its uniqueness from volcanic activities. The Congo Basin, home to some of the world’s largest tropical rainforests, also contributes to Africa’s notable topography.
Deserts Of Africa
The Sahara, the world’s largest desert, spans across North Africa. The Namib and Kalahari deserts in the south also constitute Africa’s dramatic environmental canvas, each possessing unique eco-systems that brings together diverse animal and plant species.
Africa’s Water Bodies
Water bodies in Africa play vital roles in supporting life, and promoting economic activities.
Major Rivers in Africa
Major rivers such as the Nile, the world’s longest river, crosses several countries providing water resources for agriculture. The Congo River, known for its depth, is vital for transportation, while the Zambezi River is renowned for the spectacular Victoria Falls.
The Great Lakes Region
The Great Lakes region is one of Africa’s prime freshwater ecosystems, containing lakes Victoria, Tanganyika, Malawi, and others. They support massive populations of fish and bird species, serving as significant economic resources.
Coastal Waters
Africa’s extensive coastline results in broad coastal waters, which are vital links to other continents. The warm waters of the Indian Ocean and the colder Atlantic waters facilitate varied marine ecosystems.

Natural Resources in Africa
Africa is a continent rich in natural resources, which serve as the backbone for its significant economies.
Mineral Rich Areas
Africa is reputed for its abundant mineral resources. South Africa is world-renowned for its gold, diamonds, and platinum, while Zambia and DR Congo are important copper producers.
Fertile Agricultural Lands
Highly fertile regions like the Nile Valley, parts of West Africa, and the highlands of East Africa provide favourable conditions for agriculture. These regions are the staples for the production of crops like coffee, cocoa, and various grains.
Forests and Wildlife
Africa’s wildlife richness and diversity are unmatched, making it a crucial global ecological pillar. The lush savannas, numerous national parks, and diverse species of flora and fauna make Africa a magnet for wildlife enthusiasts and researchers.
Africa’s Climate Zones
Africa spreads across both hemispheres making it a host to a wide range of climate zones.
Tropical Rainforest Climate
The tropical rainforest climate around the equator receives high rainfall throughout the year, supporting dense forests and diverse wildlife.
Savanna Climate
The savanna climate is characterized by mixed woodland and expansive grasslands, providing an ideal habitat for a variety of fauna.
Desert Climate
The desert climate is found in the Sahara and the Kalahari, characterized by extreme temperature fluctuations and scarce rainfall, with a unique array of adapted life forms.

Physical Map Symbols
It is essential to understand the physical map symbols to interpret Africa’s topographic details accurately.
Interpreting Topographic Symbols
Each symbol on the map represents a particular geographic feature. For example, short, straight lines depict the presence of mountains, while wavy ones symbolize rivers.
Colour Codes in Physical Map
Maps often use different colours to differentiate the topographic features. Typically, green denotes low-lying land areas while brown or white highlights high elevations or snow-capped mountains.
Population Distribution in Africa
In terms of population, Africa is diverse, showcasing a striking rural-urban divide.
Population Density Regions
Despite its vast size, Africa’s population is unevenly spread with significant clusters in fertile regions like the Nile Valley, coastal regions, and the Great Lakes region.
Rural vs Urban Populations
While urbanization is on the rise, the rural population remains significant. Rural populations generally engage in traditional subsistence farming, while the urban settlements, like Lagos and Johannesburg, are industrial and commercial hubs.
Physical Impact on Africa’s Culture and Lifestyle
The physical features profoundly influence Africa’s culture, lifestyle, and settlement patterns.
Influence of Topography on Settlements
Topography impacts settlement patterns, with most populations preferring fertile, flat regions that support agriculture. Areas near rivers and lakes are also common places of settlement.
Impact of Climate on Farming and Food
The climate influences agricultural practices and dietary preferences. Rain-fed agriculture thrives in the fertile, tropical regions while animal herding is common in the arid and semi-arid regions.
Impact on Transportation and Communication
Physical geography also significantly impacts transportation and communication across Africa.
Influence of Rivers and Lakes on Transportation
Africa’s rivers and lakes serve as important transportation routes, promoting trade and travel between regions and countries.
Impact of Mountains and Valleys on Communication
Mountains and valleys, however, can pose challenges for ground transportation; they can also obstruct telecommunication signals, making digital communication difficult in certain areas.
Africa’s Geographic Challenges
Despite its rich resources, Africa faces numerous geographical challenges.
Consequences of Desertification
Desertification threatens agricultural activities and human settlements, mainly near the Sahara and Kalahari deserts.
Climate Change and its Effects
Climate change impacts Africa significantly, marked by increased droughts, floods, and shifts in rainfall patterns, adversely affecting agriculture and food security.
Notations and References
Understanding accurate geographical representations is crucial for anyone exploring Africa’s physical features.
Understanding Map Notations
Grasping map notations, including contour lines, scale indicators, and symbols, is key for comprehending a region’s physical character.
Useful References and Resources
Reliable geographical references and resources, such as the African Physical Map, offer valuable insights into the continent’s geographical make-up, and serve as a basis for further exploration in related fields.